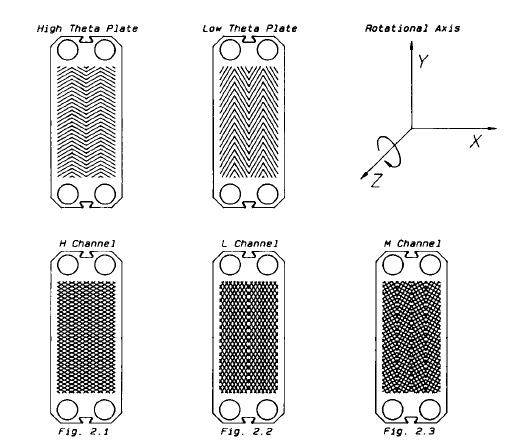
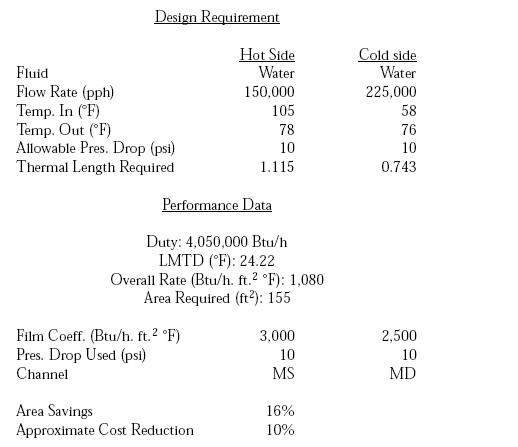
Asymmetric Plate Heat Exchangers

Plate heat exchangers (PHE) consist of a series of thin corrugated plates hung from a carrying bar and clamped between a fixed and movable head plate. The corrugated plates or heat transfer plates are normally stainless steel or other materials ductile enough to allow pressing. Each heat transfer plate is fitted
with an elastomeric gasket, partly to seal and partly to distribute the process fluids. Connections in the fixed or movable head plates permit the entry of the process fluids into the plate pack. Differentiating a heat transfer plate from a channel is extremely important and fundamental to the analysis of PHEs. The heat transfer plate separates the two process fluids; the channel is the space established by two heat transfer plates, through which process fluids are distributed and heat transfer is carried out. Figure 1 details the major components of a PHE. Nomenclature describing PHEs is not standardized, and alternate names are used by various manufacturers.